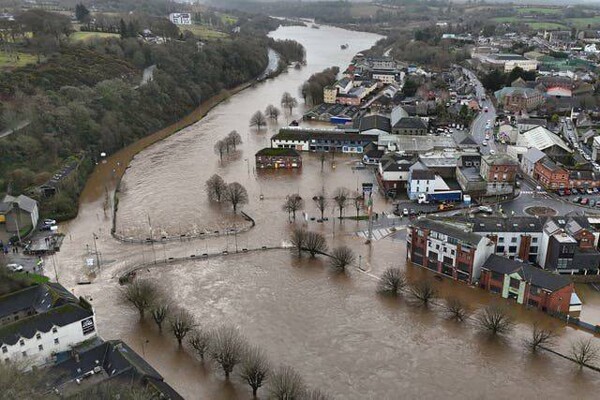
A British study has revealed that root canal treatment helps lower blood sugar levels and prevent heart disease and other chronic illnesses.
As noted, there are other benefits related to inflammation, a factor that causes cardiovascular diseases and other chronic conditions. But what is root canal inflammation?
Root canal inflammation is an infection that occurs in the tooth's pulp due to deep cavities or cracks, causing pain or swelling in the gums.
Inflammation markers, which are a contributing factor to many chronic diseases, also decreased after dental treatment. According to experts, these findings are of great importance to global health, as chronic dental inflammation often goes untreated.
Root canal treatment is one of the most common dental procedures, performed to treat inflammation or damage to the tooth's pulp—the soft inner tissue containing nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
According to a 2024 public health survey, over a third of adults in England received root canal treatment, with the rate rising to 50% among those aged 55 to 74.
A British study found that root canal treatment, a common procedure for dental infections, helps reduce blood sugar levels and protect against heart disease and other chronic conditions.
The study, published in The Guardian and tracking patients with the infection over two years, showed a decrease in blood sugar levels, suggesting that removing bacteria that cause various health issues may help prevent type 2 diabetes.
Dentists also noted improvements in patients' cholesterol and blood fatty acid levels, both linked to heart health.
However, it was unclear whether root canal treatment had benefits beyond treating dental inflammation.
In a study published in the journal Translational Medicine, researchers observed significant changes after root canal treatment in more than half of the blood molecules they analyzed.
Before and four days after the procedure, they analyzed patients' blood molecules to understand how their bodies processed sugar, fats, and other substances.
Dentists explain that chronic dental infections can allow bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Once spread, these microbes can increase inflammation and impair the body's ability to regulate blood sugar.
According to the World Health Organization, 3.7 billion people worldwide suffer from untreated oral diseases.
The results indicate short-term improvements in fat metabolism and long-term improvements in blood sugar levels.
Given the broader health impact of dental inflammation, oral health should be integrated into a patient's general healthcare.
In the United States, over 15 million root canal procedures are performed annually.
Researchers followed 65 patients from Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust for two years after their root canal treatment.














